Explain Different Operations of Cellular System
For systems primarily designed for voice latency was a main concern and modulations were chosen to be reliable and operating well at fairly low SNR like QPSK. 21 shows with connections to link the three subsystems.
Describe the principle of operation of cellular mobile system and explain the cellular concept with a neat diagram.
. Out of total radio channels say 416 available for a cellular coverage area few channels say 21 are designated for setting up connections and are called as set-up-channels. CMC UNIT WISE Important Questions Answers -. The users signal power is concentrated in a relatively narrow frequency band.
On the silicon a PN positive-negative junction was formed as a potential barrier. A mobile unit a cell site and a mobile telephone switching office MTSO as Fig. They may be used to fill in a hole in the coverage in the cellular system or to address a problem such as the entrance to a tunnel etc.
The ratio of EMF at the receiver input to the intensity of the electric field that occurred on the antenna is known as the receivers. It is very common to find five to ten microcontrollers in a low-cost cellular telephone. The third-generation 3G networks integrate cellular and PCS voice services with a variety of packet-switched data services in a unified network.
Mobile Telephone Service MTS Improved Mobile Telephone Service IMTS MJ systems and Improved Mobile Telephone Service IMTS MK systems. When a mobile moves into a different cell while a conversation is in progress the MSC automatically transfers the call to a new channel belonging to the new base station. Handoff operation identifying a new base station re-allocating the voice and control channels with the new base station.
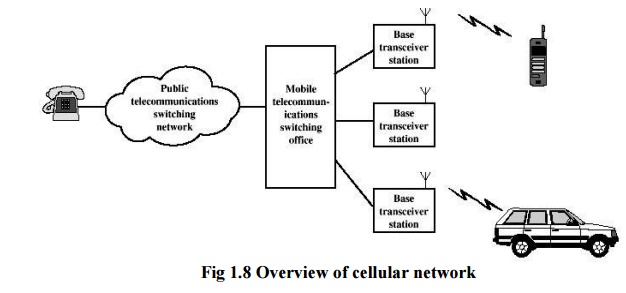
A basic analog cellular system 1 2 3 consists of three subsystems. The specifications must protect the value of operators investments in spectrum by managing unwanted emissions and incoming interference ensuring that devices and networks behave in a predictable manner and ensuring a basic level of efficiency in using. OFDM is a multi-cellular transmission technique where a data stream is carried with many lower-rate subcarrier tones.
A Mobile Station MS A mobile station is basically a mobilewireless device that contains a control unit a transceiver and an antenna system for data and voice transmission. Six basic components of Cellular Systems. Deployment and operation of cellular systems require carefully deviced radio requirement and conformance specifications.
Later on the need for an European public land mobile system was realized. The architecture of most cellular systems can be broken down into the following six components. A Mobile Station MS A mobile station is basically a mobilewireless device that contains a control unit a transceiver and an antenna system for data and voice transmission.
Public Switched Telephone Network PSTN Network Switching System NSSMobile Telephone Switching Office MTSO Base Station System BSS Mobile Stations MS Terminologies related to Cellular Systems. Components of a Cellular System. Photons falling on the PN junction cause the rise of pairs of opposite electrical charge carriers electron hole which as a result of the presence of PN junction are separated in two different directions.
Cellular System Architecture. The effective length is the parameter of antennas that characterizes the efficiency of the antennas in transmitting and receiving electromagnetic waves. Principle of operation of photovoltaic solar panels The photovoltaic phenomenon was discovered in 1839 by Edmund Bequerel who noticed that the sun produces electrical energy under certain electrochemical configurations.
In 1982 the Conference of European Posts and Telegraphs CEPTformed a study group called the. Wireless networks are slowly developing from 1G analog. Q Co-chl interference reduction factor.
All the analogue cellular systems used FDMA system. Operation of Cellular Systems The Operation of a cellular system can be divided into four parts besides a handoff procedure. Both provide 11 channels.
We assume a cellular system having a cell radius R and Co-channel distance D and the cluster size N. The second-generation 2G wireless networks are voice-oriented digital cellular and PCS systems and data-oriented wireless WANs and LANs. Since the cell size is fixed co-channel interference will be independent of power.
IMTS MK operates at 450 MHz and provides 12 channels. Different users are assigned different channels on demand basis. Co-chl interference is a function of q DR.
The architecture of most cellular systems can be broken down into the following six components. Photovoltaic cell consists of high-purity silicon. The 2G GSM has 125 channels in the uplink and 125 channels in the down link.
Digital signal processing is also used in many contexts in cellular telephone systems for instance speech coding in mobile or global systems for mobile communication GSM telephones modulators and demodulators voice scrambling and other cryptographic devices. System to 3G high-speed digital networks a nd now going towards 4G. MTS operates around 40 MHz and MJ operates at 150 MHs.
Six basic components of Cellular Systems. For data systems it is advantageous to take advantage of higher modulation schemes such as 16QAM and 64QAM when the radio link allows it. What is the total bandwidth occupied in both uplink.
A mobile telephone unit contains a control unit a transceiver and an antenna system. Another type of cells known as an umbrella cell is sometimes used in instances such as those where a heavily used road crosses an area where there are microcells. Each channel has a bandwidth of 200 kHz.
Effective length can be defined for both transmitting and receiving antennas. In the beginning around 1980s analog cellular telephone systems were developing in Europe and each country was developing its own system and thus making them confined within their country boundaries. The photovoltaic phenomenon was started to be used to turn direct sunlight into energy since 1954.
Under normal circumstances this would result in a large number of. Co-Channel Interference and Cell Separation. Base Transceiver Station BTS BTS provides physical connection between MS to network using Air Interface Um Main function of BTS is for maintaining the Um interface and minimizing the transmission problem Um very sensitive for disturbance Using Abis interface for connection between BTS and BSC.

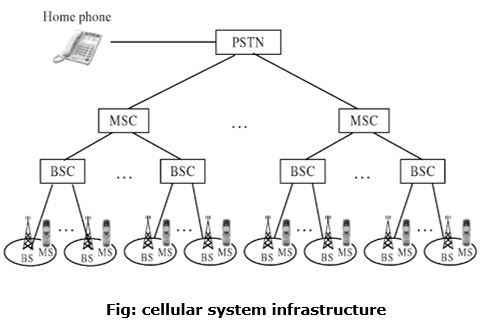
Cellular System Infrastructure Javatpoint

0 Response to "Explain Different Operations of Cellular System"
Post a Comment